Model Contribution APIs
Introduction
Developers can use standard HST APIs such as HstRequest#setModel(String, Object) and HstRequestContext#setModel(String, Object) in HstComponents to participate in contributing content items or domain-specific models to the aggregated page model representation.
HST Model Contribution APIs
The following methods are available in HstRequest/HstRequestContext for model contriubtion to Page Model JSON API:
/**
* Returns the model object associated with the given {@code name},
* or <code>null</code> if no model object of the given {@code name} exists.
*
* @param name the name of the model object
* @return the model object associated with the {@code name}, or
* <tt>null</tt> if the model object does not exist.
*/
<T> T getModel(String name);
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable <code>Iterable</code> containing the
* names of the model objects available to this.
* This method returns an empty <code>Iterable</code>
* if this has no model object available to it.
*
* @return an <code>Iterable</code> of strings containing the names
* of model objects of this.
*/
Iterable<String> getModelNames();
/**
* Returns an unmodifiable map of model objects contributed by {@link #setModel(String, Object)}.
* <P>
* Note that the returned map contains only the pairs of model name and value objects contributed by {@link #setModel(String, Object)},
* but it does not contain attributes set by <code>#setAttribute(String,Object)</code> API calls, whereas most
* implementations of this interface (such as {@link HstRequest} and {@link HstRequestContext}) provides a
* combined view for both <code>models</code> and other <code>attributes</code> through <code>#getAttribute(String)</code>,
* <code>#getAttributeNames()</code> or <code>#getAttributeMap</code>.
* </P>
* @return an unmodifiable map of model objects contributed by {@link #setModel(String, Object)}
*/
Map<String, Object> getModelsMap();
/**
* Stores a model object in this.
* <p>
* Model objects are contributed by a controller component to this, in general.
* And, the contributed model objects may be accessed in view rendering or special model
* aggregation / serialization request pipeline processing.
* </p>
* <p>
* If the model object passed in is null, the effect is the same as
* calling {@link #removeModel}.
*
* </p>
* @param name the name of the model object
* @param model the model object to be stored
* @return the previous model object associated with <tt>name</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>name</tt>.
*/
Object setModel(String name, Object model);
/**
* Removes a model object from this.
*
* @param name a <code>String</code> specifying
* the name of the model object to remove
*/
void removeModel(String name);
To contribute any objects (content documents, folders, gallery images, assets or any domain-specific POJO objects) from your HstComponent, use #setModel(String name, Object model) method in your component class. Then the model object will be included in the models field inside the specific component representation. If the model object is a WCMS content document, folder, gallery image or asset, the model representation in the models field will include only a JSON Pointer reference as JSON String (e.g, { "$ref":"/content/ub89d576f680a4bbf9c272dced9da3d6c" }) while serializing the real content data in the top level content field.
For details on how model objects are serialized into JSON, see Model JSON Mapping Details.
Model Objects Must Be JSON-Serializable
When contributing a domain-specific POJO object through HstRequest#setModel(String name, Object model), the model object must be serializable to JSON for Page Model JSON API. Otherwise, Page Model JSON API will fail to serialize the whole JSON output.
Internally, Page Model JSON API serializes all the aggregated model objects to JSON by using the com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper bean. Therefore, make sure that your domain-specific POJO model object can be written to JSON through com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper#writeValue(Writer out, Object model). In most cases where your domain-specific POJO model consists of only basic types such as String, Number, Calendar or compound classes having those basic types as well, you won't have any problem in JSON Serialization as Jackson library will handle those basic types automatically. However, if you have any non-JSON-serializable properties for some reason, then you should exclude or convert those properties properly. One of the simplest approaches with Jackson library is to use @JsonIgnore annotation (see Jackson Annotations for more details) to exclude those in your model class.
Suppose you have a custom document bean, ProductBean, extending HippoDocument, with a non-JSON-serializable property like the following:
public class ProductBean extends HippoDocument {
// SNIP
/**
* As an imaginary scenario, you have a getter method (as a result, working as a read property)
* that retrieves CSV data stream from an external PIMS (Product Information Management System) for this product.
* @return PIMS data stream in CSV for this product
*/
public InputStream getPimsDataInCSV() {
// retrieve CSV data from PIMS and return it as an InputStream.
}
}
Now, the property, pimsDataInCSV, is not desirable to serialize and cannot be serialized into JSON properly through com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper. The easiest solution to this problem is to annotate the getter method with @JsonIgnore like the following:
public class ProductBean extends HippoDocument {
// SNIP
/**
* As an imaginary scenario, you have a getter method (as a result, working as a read property)
* that retrieves CSV data stream from an external PIMS (Product Information Management System) for this product.
* @return PIMS data stream in CSV for this product
*/
@JsonIgnore
public InputStream getPimsDataInCSV() {
// retrieve CSV data from PIMS and return it as an InputStream.
}
}
Then Page Model JSON API will exclude the unnecessary property when serializing your domain-specific POJO model object.
- README.md of jackson-databind module.
- Jackson Annotations
- Jackson Mixin Types (JacksonMixInAnnotations)
- Jackson Serialization
Model Contribution, Aggregation and Serialization Phases
On a high level, there are three phases in Page Model JSON API processing:
- Component Model Contribution Phase
- Page Model Aggregation Phase
- Page Model Serialization Phase
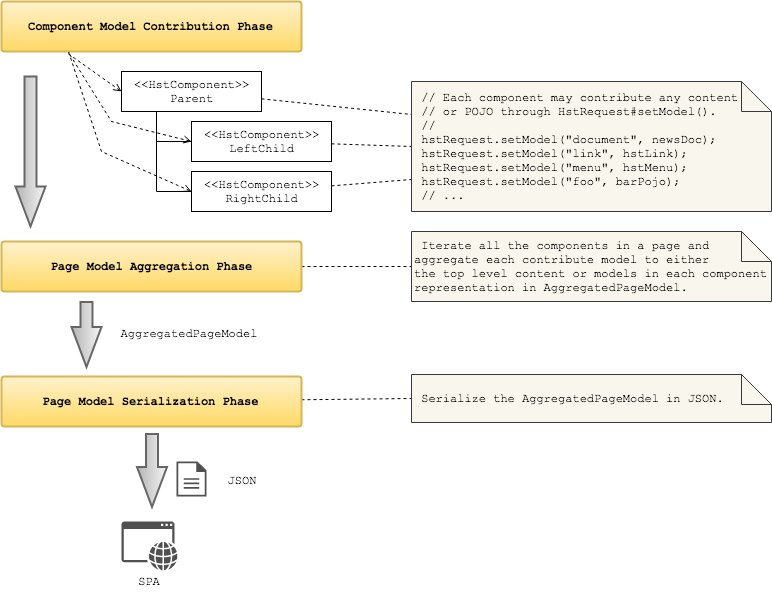
In the Component Model Contribution Phase, HST Container invokes the #prepareBeforeRender(HstRequest, HstResponse) and #doBeforeRender(HstRequest, HstResponse) method on each HstComponent instance. If an HstComponent instance contributes any models through HstRequest#setModel(String, Object) method, the model object will be accumulated in HstRequest level and also it is set to an attribute of HstRequest as well. So, the HstComponent does not need to invoke #setAttribute(String, Object) again for the contributed model object.
In the Page Model Aggregation Phase, HST Container iterates all the HstComponents in a page, gathers all the contributed model objects in each HstComponent and aggregates all the models into AggregatedPageModel object.
Finally, in the Page Model Serialiation Phase, HST Container serializes the AggregatedPageModel object into JSON resource for SPAs. For details on how model objects are serialized into JSON, see Model JSON Mapping Details.
Summary
HstRequest provides an intuitive model contribution API, so HstComponent can contribute any model objects to Page Model JSON API. On a high level, the whole Page Model JSON API processing consists of the three phases: (1) Component Model Contribution Phase, (2) Page Model Aggregation Phase, and (3) Page Model Serialization Phase. In the Component Model Contribution Phase, HstComponents may contribute any models through HstRequest#setModel(String, Object) method, and the contributed model objects will be accumulated in HstRequest level. Finally, all the contributed model objects will be aggregated into AggregatedPageModel in the next phases to serialize into JSON resource for SPAs.

