Deploy the Authoring and Delivery Web Applications Separately
Introduction
Goal
Deploy the authoring and delivery applications in separate containers.
Background
Typically, Bloomreach Experience Manager's authoring (cms) and delivery (site) applications are deployed together on the same server. The delivery application has access to the repository which is hosted by the authoring application. However there are use cases where deploying the authoring and delivery applications separately on different application servers is preferable. For example you may want to deploy the delivery application on multiple servers to increase availability. In these cases the delivery application is deployed without the authoring application, therefore it cannot access the platform hosted by the latter.
The solution is to package the platform as a separate web application and deploy it together with the delivery application. The platform webapp will provide for access from the delivery application to the underlying storage repository.
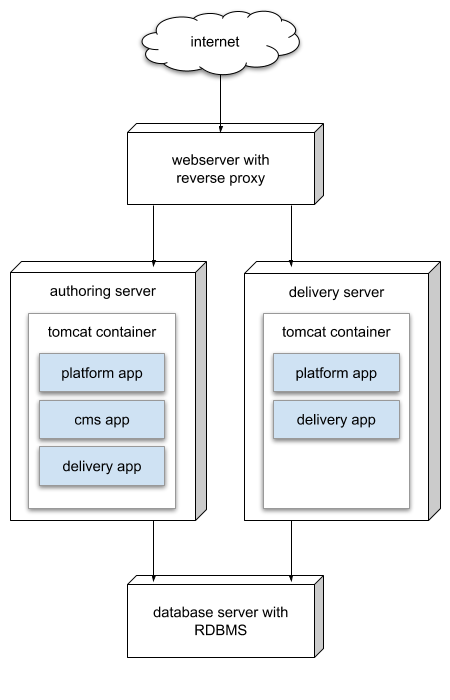
Requirements
- The platform webapp must be backed by a supported database and configured for clustering. See Configure Bloomreach Experience Manager for your Database Server for sample configurations for supported databases.
- The authoring cluster must be started before the delivery cluster.
Deployment
The project should be delivered as two separate distributions for the authoring and delivery applications. These two tar.gz files contain the web applications for each server. Deploy the cms and site WARs to the first server, and the site and platform WARs to the second.
Take special care to:
- Specify the location of your repository.xml on both servers. This is done with the system property repo.config as mentioned in Configure the Application Server (Apache Tomcat on Linux).
-
Disable bootstrapping on the delivery server (start it with the option -Drepo.bootstrap=false).
Always start up the container hosting the delivery application (site.war) with bootstrapping disabled, i.e. with -Drepo.bootstrap=false.
If you would enable bootstrapping for the delivery application, the following undesirable scenario would unfold:
The bootstrap process removes all YAML definitions from the repository that it can't find on the classpath; because you have a limited set of artifacts on the repository classpath, a lot of YAML definitions will be removed including the bootstrapped nodes by those YAML definitions; next time you start up the authoring node, where these YAML definitions items are on the classpath, the bootstrap process will re-import those YAML definitions because it can't find them in the repository anymore and the earlier removed nodes will be bootstrapped again. -
Make sure the authoring clusters are started before starting the delivery clusters.
Disabling Scheduled Jobs on the Delivery Nodes
By default all platform instances perform scheduled tasks in a clustered repository setup. Scheduled tasks are amongst others: scheduled (de-)publications, repository maintenance jobs, checking for brokenlinks, etc. In case you want to be sure that these actions do not run on the delivery nodes, you can disable this behaviour by adding the following directive to the startup script of the application container.
-Dhippo.scheduler.disabled=true

